Mechanisms of low level light therapy
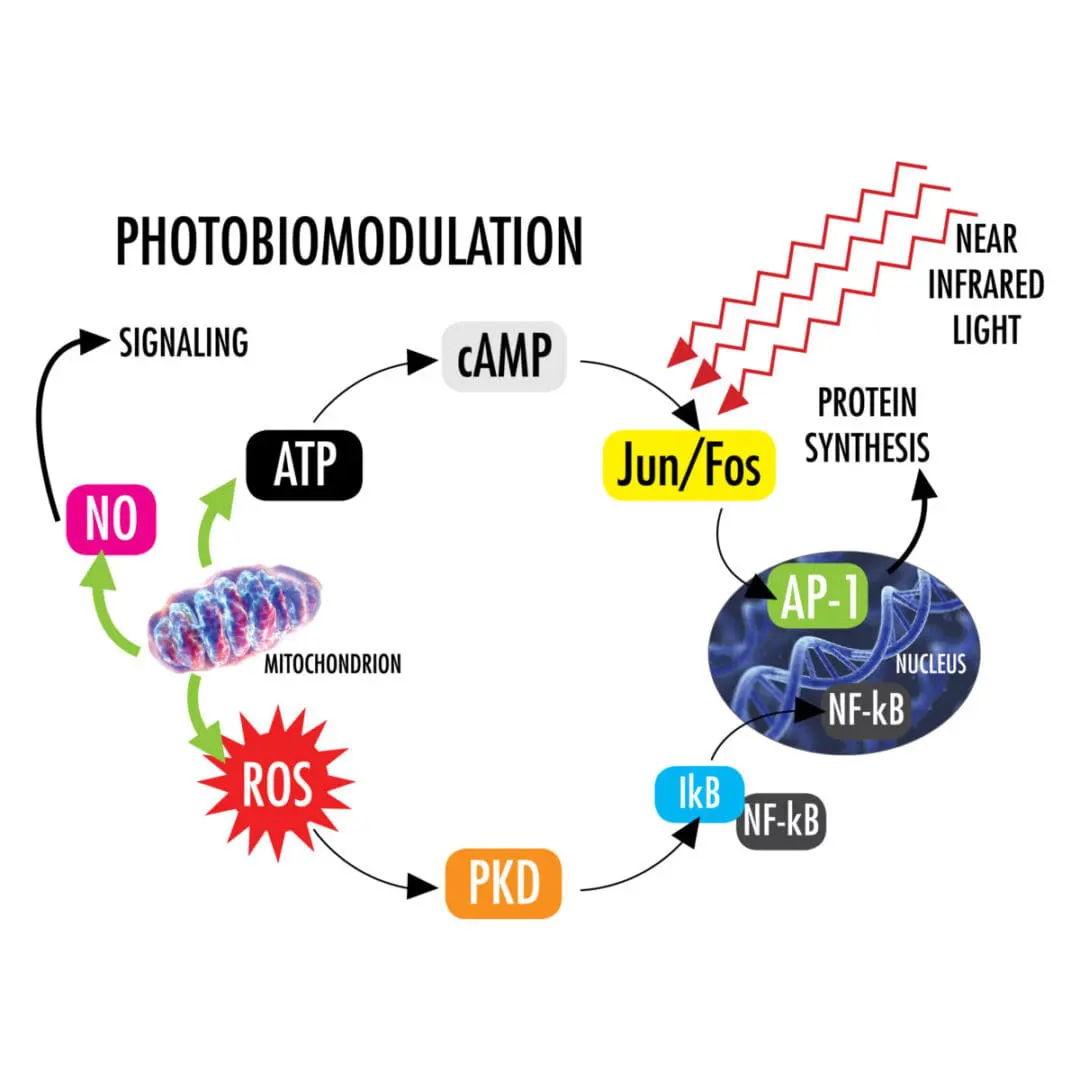
This review paper covers the current theory on basic mechanisms of laser therapy. Cytochrome C oxidase is identified as the primary absorber of light in the near infrared leading to cellular changes related to ATP, NO and ROS levels. The “optical window” for tissue penetration is identified from 600 nm to 1.4 mm. A review of animal and clinical studies is also presented for applications including wound healing, nerve regeneration and numerous musculoskeletal conditions.
Published: Proc. of SPIE Photonics. 2006; 6140: 614001-01-12. doi: 10.1117/12.646294
Comments